SecurityContextHolder와 Authentication
SecurityContextHolder

SecurityContext 를 제공. 기본적으로 ThreadLocal을 사용하기 때문에 SecurityContext는 동일 쓰레드 내에서 항상 접근이 가능
SecurityContext
Authentication을 제공
// SecurityContextHolder -> SecurityContext -> Authentication
Authentication authentication = SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication();
// Principal
Object principal = authentication.getPrincipal();
// GrantedAuthority의 리스트 (한 사용자는 여러 권한을 가질 수 있기 때문)
Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> authorities = authentication.getAuthorities();
// Credentials - 인증 정보 (인증 후엔 null)
Object credentials = authentication.getCredentials();
// 인증 여부
boolean authenticated = authentication.isAuthenticated();Authentication
사용자의 인증 정보를 저장하는 토큰의 개념 (인터페이스). 사용자 별로 별개의 Authentication이 생성된다. 내부에 크게 2가지 정보 - Principal과GrantAuthority를 저장한다. Form 인증 방식에서는 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken이 구현체로 사용된다.
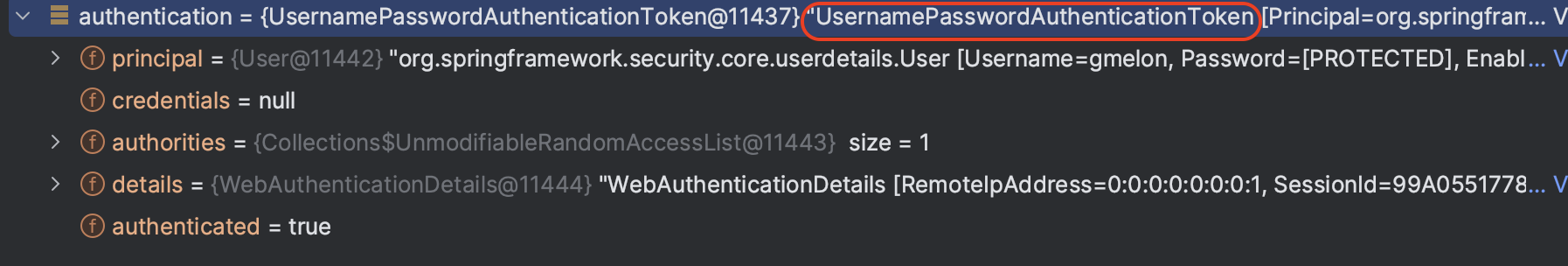
사용자 별 Authentication객체를 구분하는 방법으로, SecurityContextHolder가 ThreadLocal에 저장되기 때문에 각각의 쓰레드 별로 SecurityContextHolder 를 가질 수 있다. (기본 모드인 MODE_THREADLOCAL에서는 다른 쓰레드에서는 접근 불가)
SecurityContextHolder 에는 반드시 인증이 된 객체가 들어가게 되어있음. 따라서, isAuthenticated() 메서드는 로그아웃 전까지는 항상 true를 반환할 것임. (다만, OAuth 방식 등의 경우 토근이 만료되면 false 반환)
Principal
인증된 사용자가 누구 인지에 해당하는 정보로 Principal 자체는 인터페이스이며 UserDetailsService에서 반환하는 UserDetails 인터페이스의 객체가 주로 구현체로 사용됨
UserDetails
유저 정보를 담는 인터페이스로, User 클래스가 구현하고 있음. Principal에 실제로 담기는 객체는 User 객체.
사용자가 구현한
유저 Entity와 시큐리티 상의유저 정보와의 어뎁터 역할을 수행함
GrantAuthority
ROLE_USER , ROLE_ADMIN 등 Principal이 가지고 있는 권한을 나타낸다. 인증 이후, 인가 과정에서 사용되는 정보
UserDetailsService
DB, 메모리, … 등 어디든지에 저장되어 있는 유저의 정보를 UserDetails 타입으로 가져오는 DAO 인터페이스. 얘를 implements 하여 repository에서 유저 정보를 가져와 UserDetails 타입으로 반환해주면, 해당 정보를 통한 실제 인증은 AuthenticationManager 가 수행한다.
AuthenticationManager와 Authentication
실제로 Authentication을 만들고 인증을 처리하는 곳이 바로 AuthenticationManager이다. SecurityContextHolder는 단순히 인증된 Authentication 객체를 들고만 있는다.
AuthenticationManager
인터페이스. 오직 하나의 메서드만을 API로 갖는다.
Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException;로그인을 시도한 유저의 username, password 를 담고 있는 Authentication(Form 인증의 경우 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken)을 받아서 인증을 수행하고 인증에 성공한다면, 인증된 정보가 들어있는 Authentication을 반환해준다. 만약 실패한다면 상황에 맞는 예외를 던진다.
ProviderManager
AuthenticationManager의 기본 구현체. 여러가지 AuthenticationProvider를 사용해 인증을 처리한다. 자신이 가지고 있는 AuthenticationProvider를 통해 인증이 불가능하면, 상위의 ProviderManager에게 반복적으로 인증 처리를 위임하는 구조로 되어있다.
AuthenticationProvider
Authentication의 구현체에 따라 인증을 처리할 수 있는 Provider 구현체가 다르다. AuthenticationProvider는 이러한 Provider들에 대한 인터페이스를 제공한다.
Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication)- 인증 처리 로직boolean supports(Class<?> authentication)- 해당 Provider가 인자로 넘어온authentication에 대해 인증을 처리할 수 있는지 여부를 반환
디버그를 통해 인증 과정 살펴보기
먼저 아래와 같이 ProviderManager의 authenticate() 메서드에 디버그를 건다.

아래와 같이 계정을 생성하고 로그인을 시도한다.
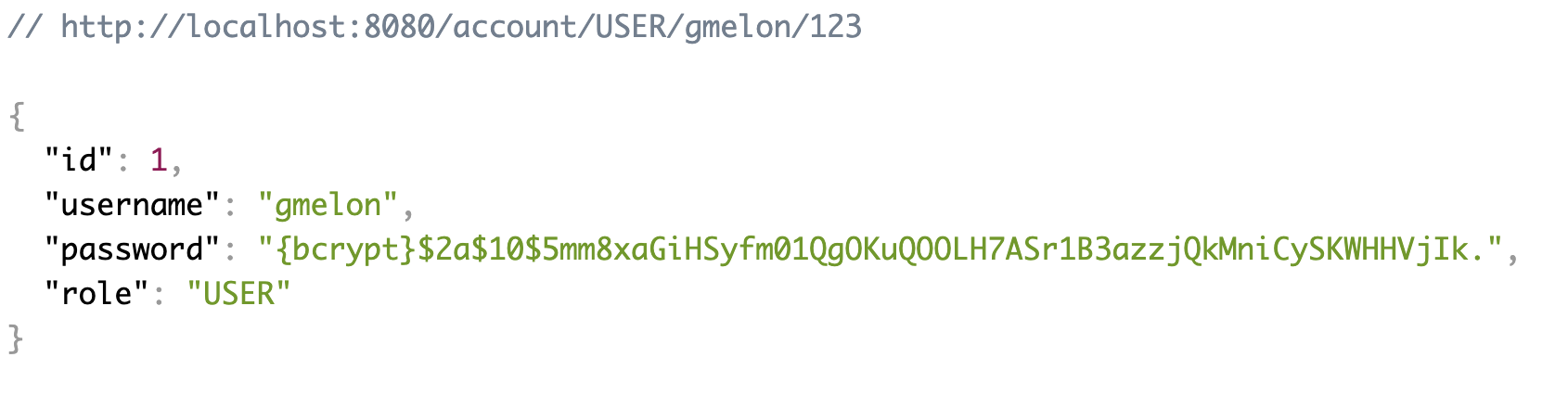
그럼 먼저 아래처럼 입력한 username, password를 가지고 있는 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken이 ProviderManager의 authenticate() 메서드로 전달된다.
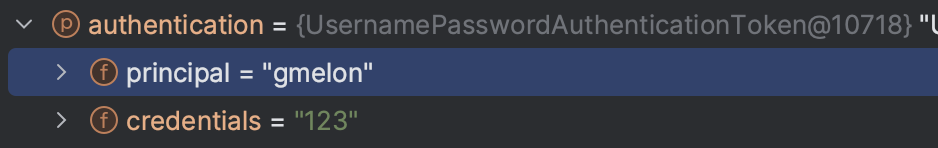
이어서 ProviderManager는 자신이 가지고 있는 AuthenticationProvider를 순회하면서 인자로 들어온 Authentication을 처리할 수 있는 AuthenticationProvider를 찾는다.
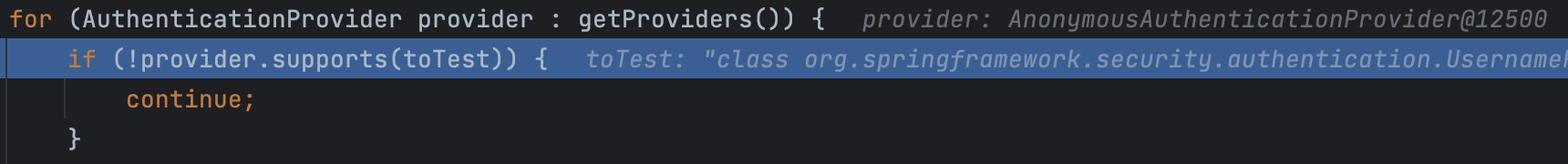
최초로 걸리는 Provider인 AnnonymousAuthenticationProvider는 Form 인증에서 사용되는 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken 은 처리하지 못한다. 따라서 아래 로직에 의해 자신의 parent Provider에게 다시 인증을 요청한다.
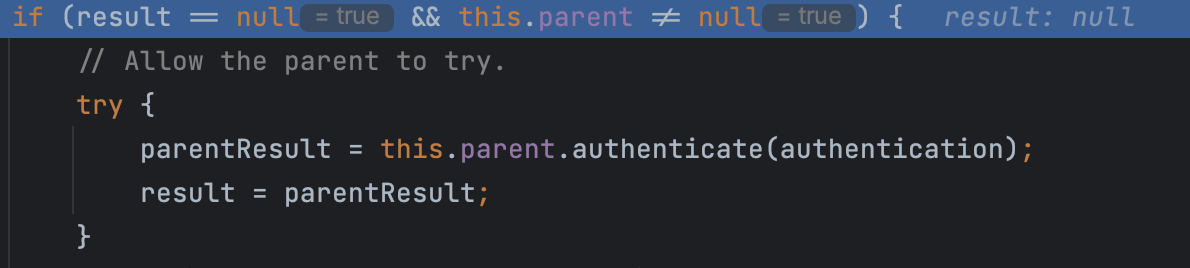
다음으로 걸리는 Provider인 DaoAuthenticationProvider는 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken 을 처리할 수 있다.
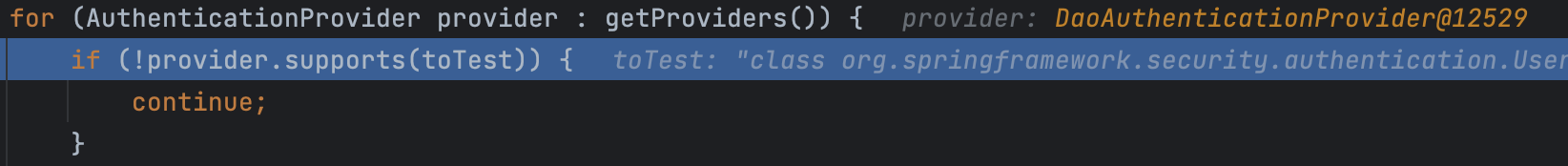
따라서 이제 실제 provider에게 인증을 요청한다.

provider의 authentication() 메서드는 몇 가지 검증, 값 대입을 수행한 후 retriveUser() 메서드를 호출한다.
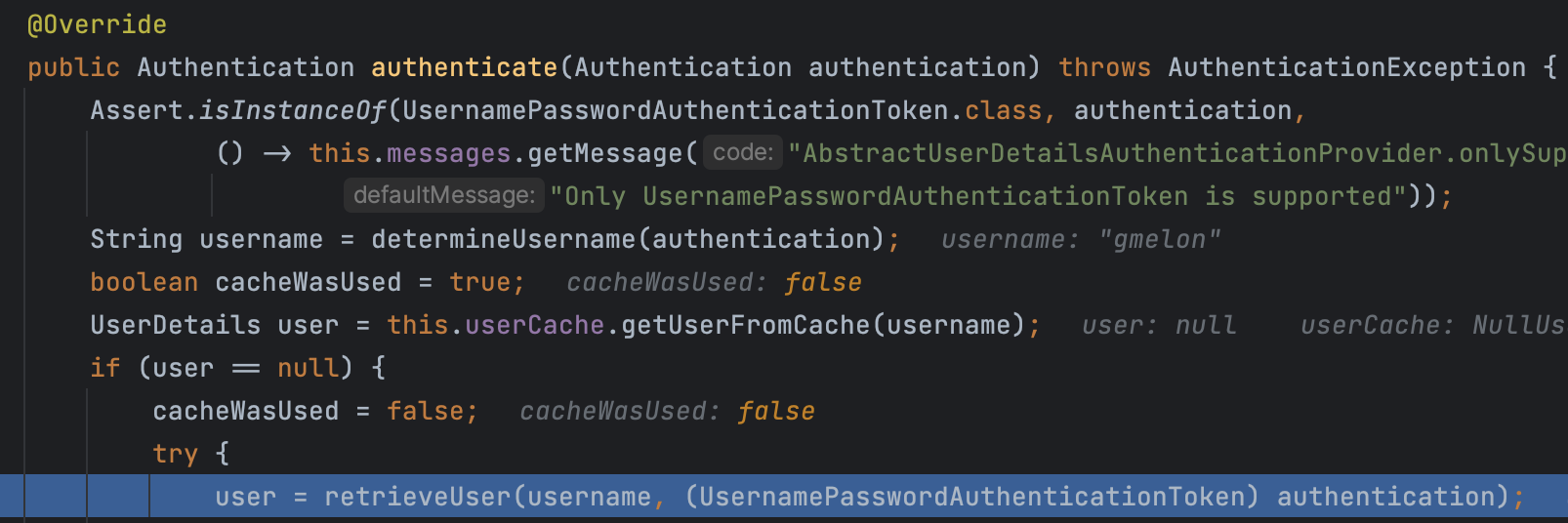
retrieveUser()은 getUserDetailsService().loadUserByUsername()을 호출하는데 여기서 호출하는 UserDetailsService가 바로 우리가 UserDetailsService를 implements 하여 작성한 코드이다.
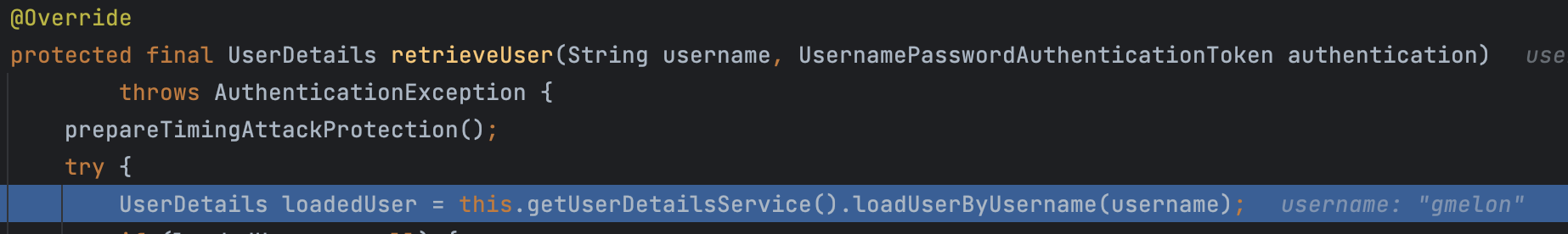
그래서 아래에 우리가 직접 구현한 AccountService implements UserDetailsService의 loadUserByUsername() 메서드가 호출되어 UserDetails를 드디어!!!! 반환한다.
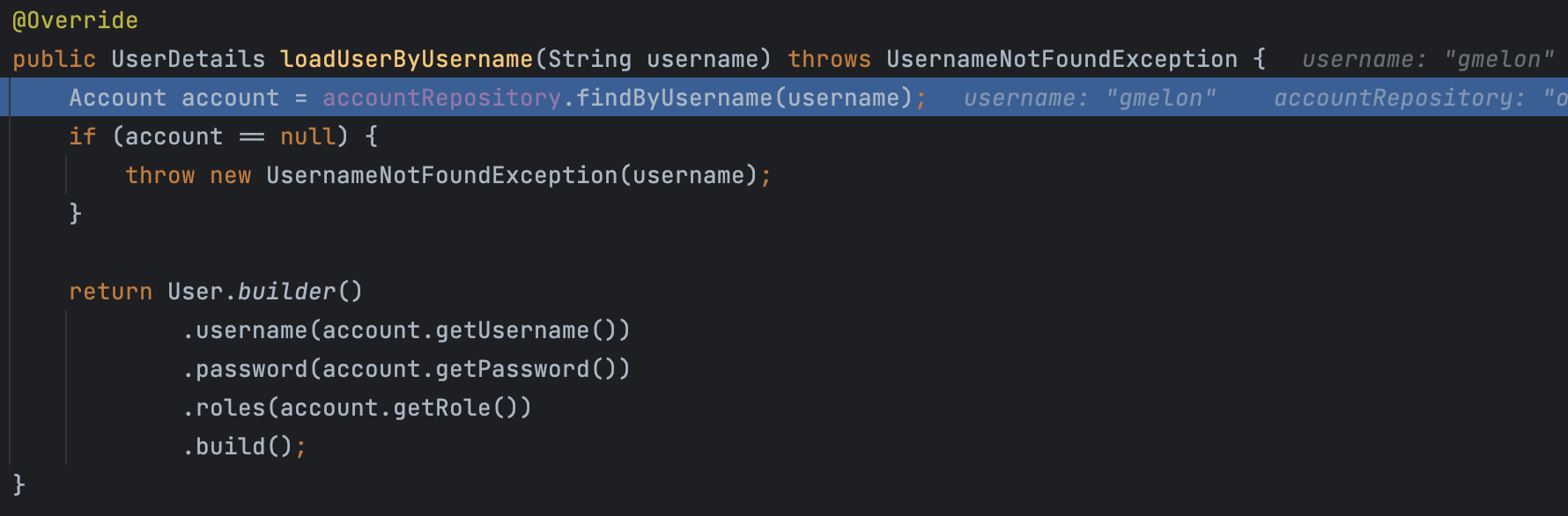
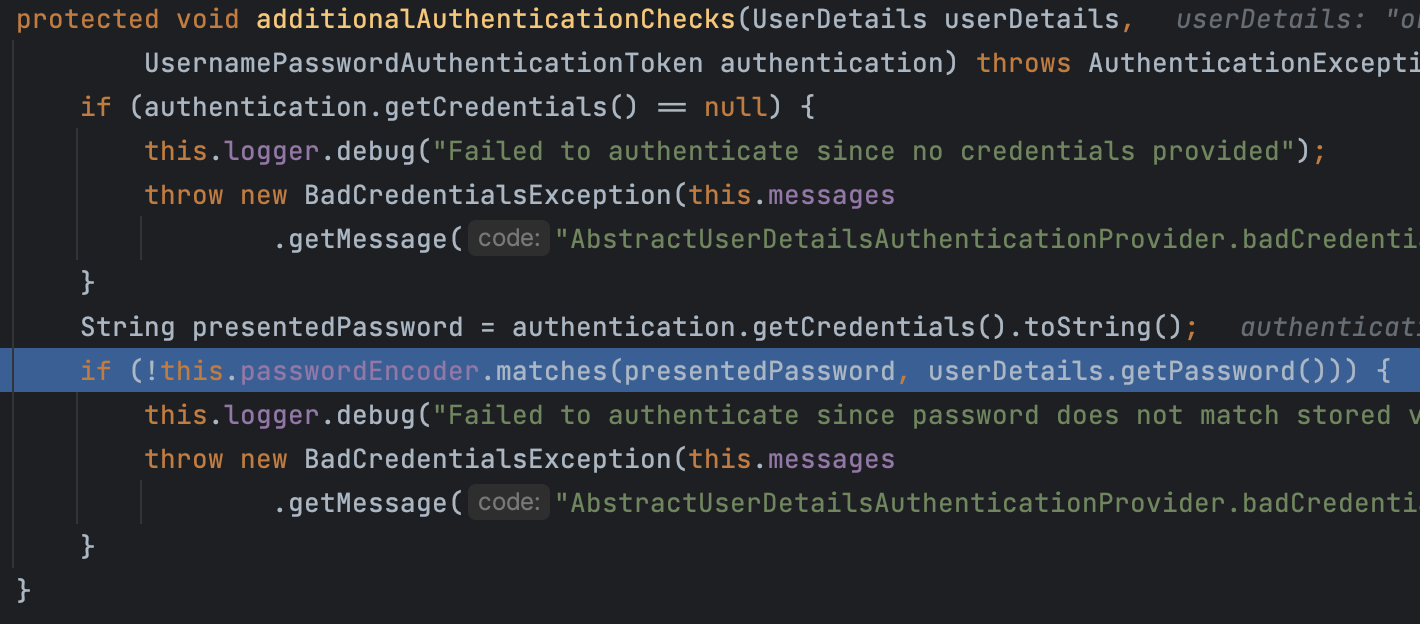
retrieveUser() 메서드가 UserDetails를 반환하면 이제 본격적으로 인증 로직이 수행된다. 구체적으로는 DaoAuthenticationProvider의 additionalAuthenticationChecks() 에서 아래와 같이 입력받은 password와 db에서 가져온 password(인코딩 과정 거침)를 비교해 일치 여부를 확인하게 된다.
계속해서 기타 나머지 인증 과정을 거쳐 모든 로직이 완료되면 아래와 같이 인증된 정보가 저장된 Authentication 객체가 SecurityContextHolder에 저장되고, 이 글 제일 처음에 작성되어있던 코드를 사용해 이를 꺼내올 수 있다.
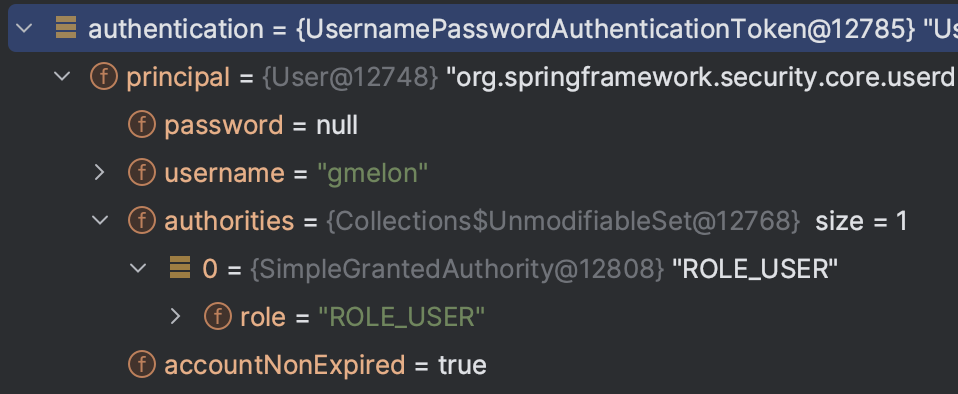
인증 전과는 달리 Principal이 단순 username을 담은 문자열이 아니라 User 객체임을 알 수 있고 GrantedAuthority 또한 ROLE_USER로 잘 들어가있는 것을 볼 수 있다.
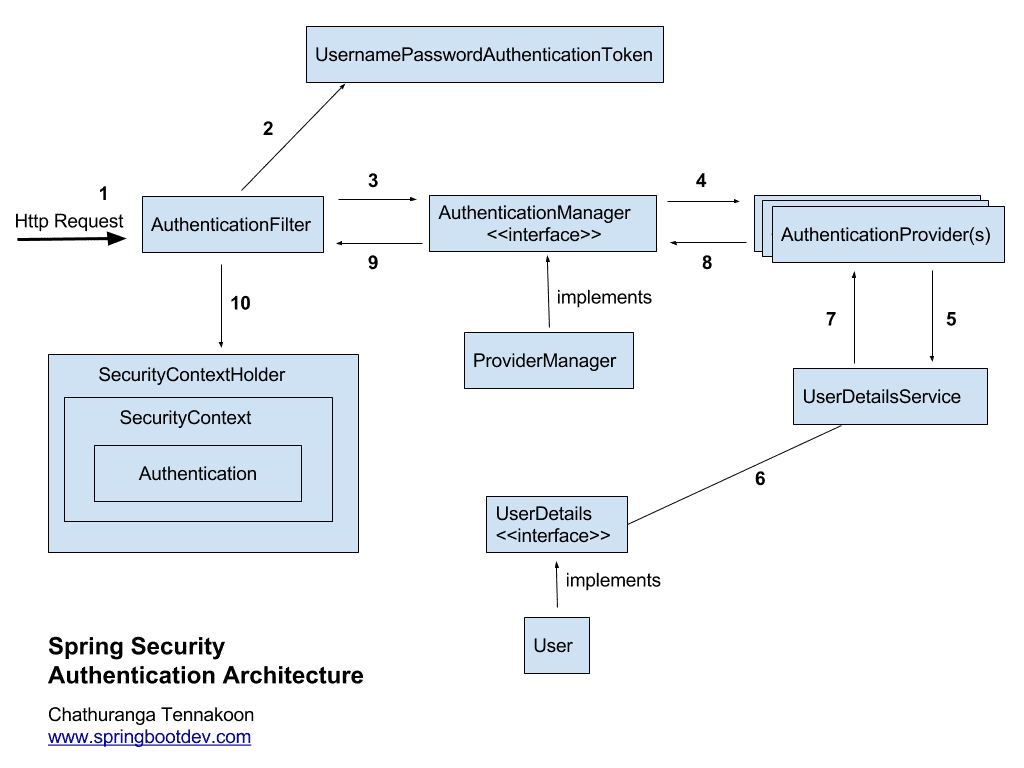
인증 아키텍처 이미지
ThreadLocal
Java.lang 패키지에서 제공하는 쓰레드 범위 변수. 즉, 쓰레드 레벨의 데이터 저장소. 같은 쓰레드에서 공유되므로 동일한 쓰레드에서 해당 변수에 접근하고자 할 때 메서드에 인자로 건네줄 필요 없이 바로 접근할 수 있음. SecurityContextHolder는 ThreadLocal를 사용해 SecurityContext를 저장하는 것이 기본 전략임.
예제를 만들어보자. 아래와 같이 Account를 저장하는 ThreadLocal를 static 변수로 갖는 유틸성 클래스를 만든다.
public class AccountContext {
private static final ThreadLocal<Account> ACCOUNT_THREAD_LOCAL = new ThreadLocal<>();
public static void setAccount(Account account) {
ACCOUNT_THREAD_LOCAL.set(account);
}
public static Account getAccount() {
return ACCOUNT_THREAD_LOCAL.get();
}
}그리고 컨트롤러에서 Principal 정보를 통해 레포지토리에서 Account를 조회하고 AccountContext에 세팅한다.
@GetMapping("/dashboard")
public String dashboard(Model model, Principal principal) {
AccountContext.setAccount(accountRepository.findByUsername(principal.getName()));
sampleService.dashboard();이어서 호출되는 sampleService.dashboard()는 아래와 같이 로직이 작성되어 있다.
public void dashboard() {
// ThreadLocal 에서 변수를 가져오는 코드
// 현재 쓰레드가 어떤 요청을 처리하는지에 따라 값이 달라진다
Account account = AccountContext.getAccount();
System.out.println("account.getUsername() = " + account.getUsername());
System.out.println("account.getRole() = " + account.getRole());
}같은 요청 쓰레드 안에서 ThreadLocal을 사용해 Account 정보를 set하고 get 했으므로 아래와 같이 account에 대한 정보가 잘 출력되는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
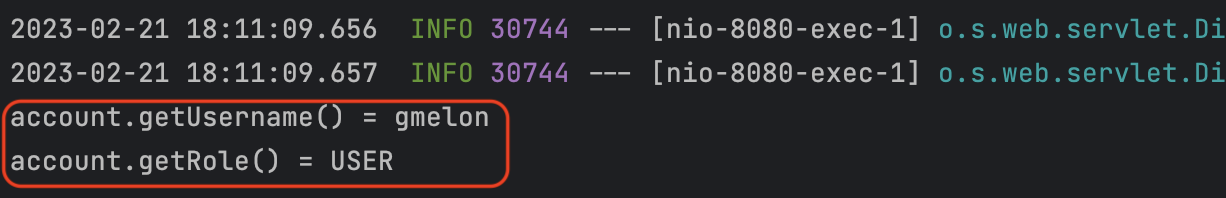
이러한 방식으로 SecurityContextHolder도 SecurityContext를 저장하고 불러와 사용할 수 있게 해준다.
Authentication과 SecurityContextHodler
AuthenticationManager 가 인증을 마치고 반환한 Authentication (Principal, Credentials, GrantedAuthorities) 객체는 누가 어떻게 SecurityContextHolder에 넣어주는가? 또, 누가 AuthenticationManager에게 인증을 하라고 명령하는가??
이에 대한 대답은 Filter 들에 있다.
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter
폼 인증을 처리하는 시큐리티 필터. 아래 코드와 같이 AuthenticationManager를 불러와 authenticate() 메소드를 호출한다. 앞서 살펴본 인증 과정은 이 필터에서 부터 시작된다.
@Override
public Authentication attemptAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws AuthenticationException {
...
// authenticate() 호출
return this.getAuthenticationManager().authenticate(authRequest);
}참고로 authRequest는 HttpServletRequest 에서 username과 password로 파라미터를 조회해 얻은 후 생성해 넣어주게 된다. (아래는 코드 일부 - 호출 순서대로 작성)
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authRequest = UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken.unauthenticated(username, password);
---
String username = obtainUsername(request);
---
protected String obtainUsername(HttpServletRequest request) {
return request.getParameter(this.usernameParameter);
}
---
private String usernameParameter = SPRING_SECURITY_FORM_USERNAME_KEY;
---
public static final String SPRING_SECURITY_FORM_USERNAME_KEY = "username";UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter 는 AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter 를 상속받고 있으며, UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.attemptAuthentication() 메소드는 AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter.doFilter()에서 호출된다. 따라서 attemptAuthentication() 메소드에서 반환된 Authentication 객체는 AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter의 아래 코드를 통해 SecurityContextHolder에 들어가게 된다.
SecurityContext context = SecurityContextHolder.createEmptyContext();
context.setAuthentication(authResult);
SecurityContextHolder.setContext(context);모든 과정이 끝나면, 로그인 수행(/login) 전 기존 요청 페이지로 리다이렉션을 수행한다.
SecurityContextPersisenceFilter
한 번 로그인 한 후 페이지를 새로고침해보자.

다시 로그인을 해주지 않아도 이전 요청 때와 동일한 Authentication 이 유지되는 것을 확인할 수 있다. 이것은 SecurityContextPersisenceFilter가 SecurityContext를 HTTP session에 캐싱(기본 전략)하여 여러 요청에서 동일한 Authentication을 공유할 수 있도록 해주기 때문에 가능한 일이다.
HTTP Session에서 캐싱된 정보를 가져오는 것은HttpSessionSecurityContextRepository를 통해 수행된다.
SecurityContextPersisenceFilter는 매 요청마다 캐싱해둔 SecurityContext를 SecurityContextHolder에 복구하려고 시도한다.
// 로그인되어 있지 않으면 contextBeforeChainExecution == null
SecurityContextHolder.setContext(contextBeforeChainExecution);그리고 모든 요청 체인이 끝나면, 아래 코드로 SecurityContextHolder를 비워주는 역할도 이 필터가 수행한다.
SecurityContextHolder.clearContext();즉,
SecurityContextPersisenceFilter가 있기 때문에 Stateless 한 HTTP 환경에서도 Stateful 하게 로그인 상태를 유지하는 것이 가능하다.
SecurityContextRepository를 교체하면 HTTP Session이 아닌 다른 곳에 Authentication 객체를 저장하는 것도 가능하다.
스프링 시큐리티 필터와 FilterChainProxy
그렇다면, 앞서 살펴본 필터는 또 어디에서 호출되는가?
FilterChainProxy
FilterChainProxy도 Filter를 구현하고 있으므로 doFilter() 메서드가 존재한다. 아래와 같이 doFilter() 메서드에서 doFilterInternal() 메서드를 호출하고
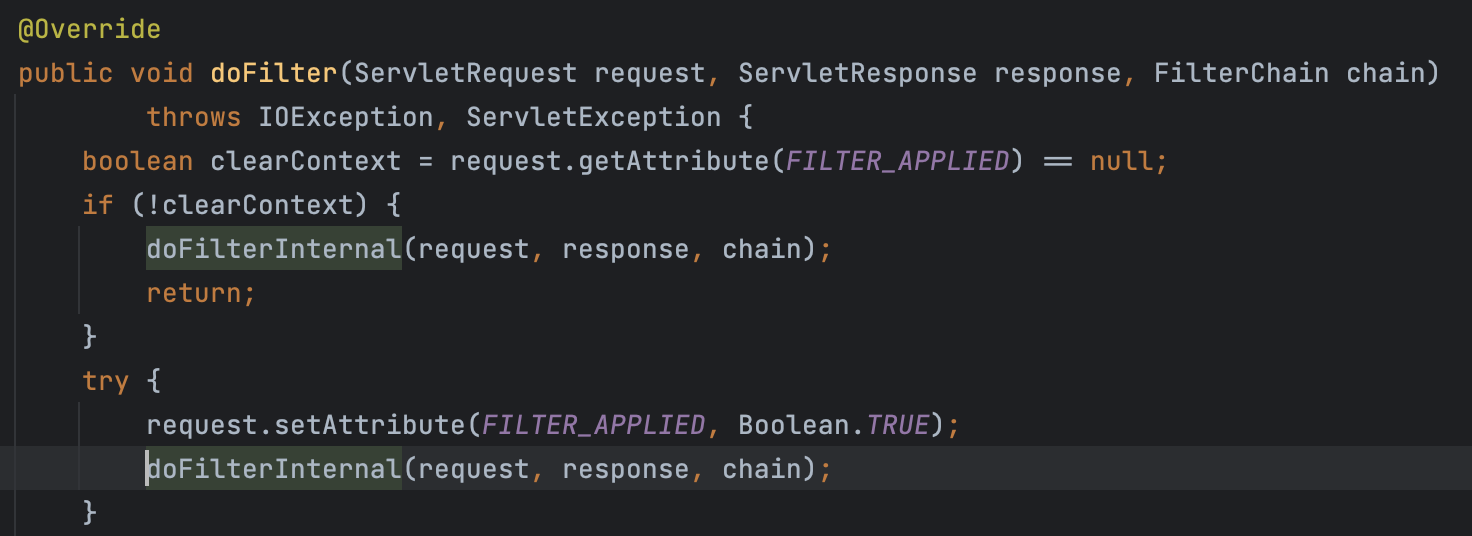
다시 doFilterInternal() 메서드에서 getFilters() 메서드를 통해 현재 등록된 체인에서 필터들을 가져오는 작업을 한 후
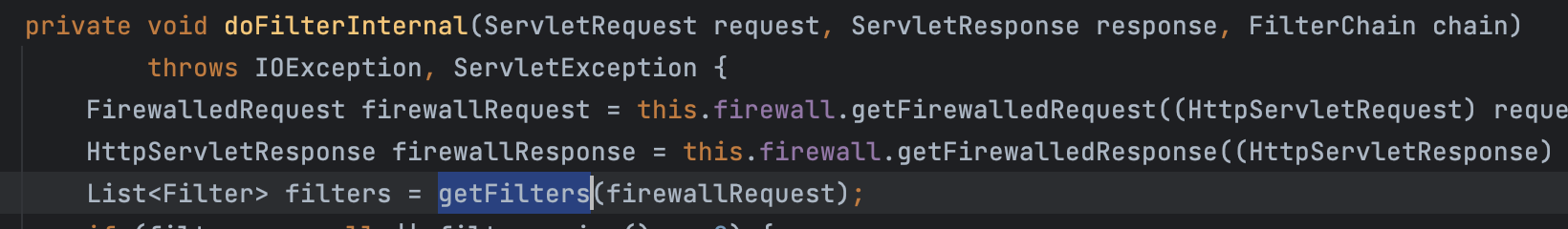
마지막으로 해당 체인의 필터들을 호출하게 된다.
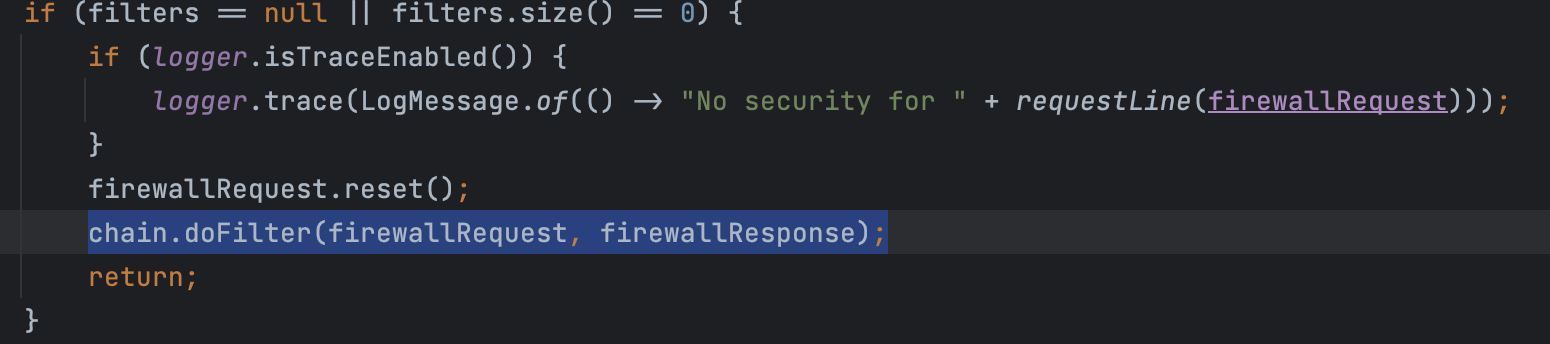
이러한 방식으로 필요한 필터들이 쭉 실행된다. 기본적으로 Form Login과 Http Basic 인증을 사용하는 경우에 체인에 등록되어 실행되는 필터들은 아래와 같다.
- WebAsyncManagerIntergrationFilter
- SecurityContextPersistenceFilter
- HeaderWriterFilter
- CsrfFilter
- LogoutFilter
- UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter
- DefaultLoginPageGeneratingFilter
- DefaultLogoutPageGeneratingFilter
- BasicAuthenticationFilter
- RequestCacheAwareFtiler
- SecurityContextHolderAwareReqeustFilter
- AnonymouseAuthenticationFilter
- SessionManagementFilter
- ExeptionTranslationFilter
- FilterSecurityInterceptor
SecurityConfig
SecurityFilterChain 을 커스텀하는게 사용됨. 하나의 설정이 하나의 Chain을 생성한다. 설정에 사용하는 .antMatcher() 가 FilterChainProxy.getFilters() 에서 요청에 매칭된 체인을 가져오는데 사용됨
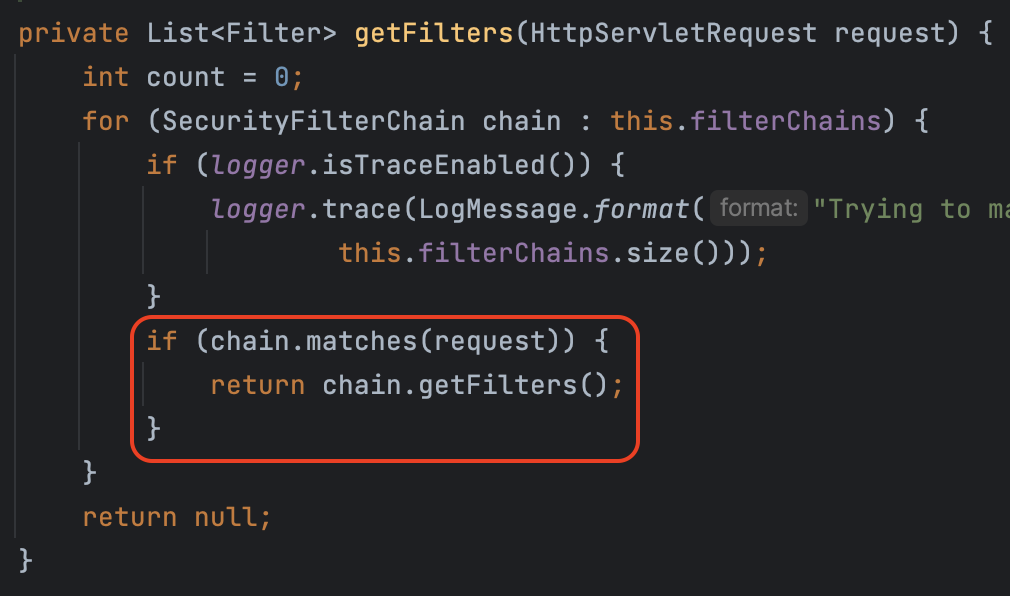
즉, SecurityConfig를 여러 개 설정하면 여러 개의 체인이 등록됨 (그 후, 요청에 따라 특정 체인에 매칭)
DelegatingFilterProxy와 FilterChainProxy
그렇다면!😂 과연 FilterChainProxy로는 요청이 어떻게 전달되는가?
서블릿 컨테이너
사용자가 서버로 요청을 보내면 서블릿 컨테이너 (ex. Tomcat) 이 그 요청을 받는다. 이러한 컨테이너들은 서블릿 스펙을 지원한다. 필터는 서블릿 스펙에서 명시하고 있는 기능이다. 필터는 간단히 말하면 특정 요청 처리 전 / 후로 특정한 작업을 할 수 있는 인터셉터 역할을 하는 객체이다.
DelegatingFilterProxy
자신이 직접 요청에 별다른 처리를 하지 않고 다른 스프링 빈에게 처리를 위임한다. 스프링 시큐리티는 DelegatingFilterProxy 를 사용해서 FilterChainProxy에게 요청 처리를 위임한다고 할 수 있다. DelegatingFilterProxy 를 사용할 땐 타겟 빔 이름을 등록해야 하는데 스프링 부트를 사용하면 SecurityFilterAutoConfiguration 이 자동으로 springSecurityFilterChain 이라는 이름으로 등록을 대신 해준다.
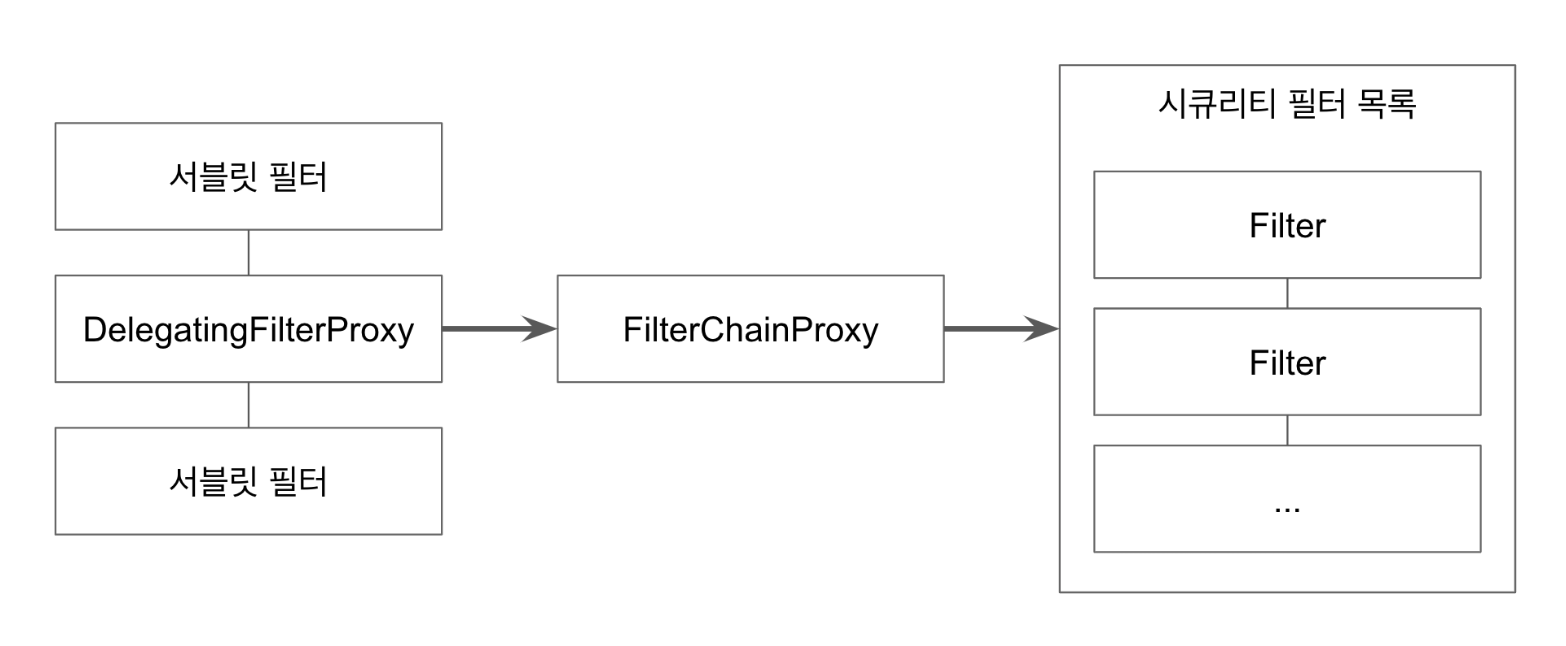
[출처 - 백기선님 인프런 스프링 시큐리티 강의]
AccessDecisionManager
이미 인증을 거친 사용자가 특정 리소스에 접근할 때 그것을 허용(인가)할 것인가? 를 결정하는 인터페이스.
즉, 인증을 처리할 땐
AuthenticationManager가, 인가를 처리할 땐AccessDecisionManager가 사용된다
아래와 같이 decide() 메서드를 통해 인가 여부를 반환한다.
void decide(Authentication authentication, Object object, Collection<ConfigAttribute> configAttributes) throws AccessDeniedException, InsufficientAuthenticationException;기본 구현체는 3가지가 존재. 몇 개의 AccessDecisionVoter 가 동의를 해야 권한을 인정할지에 따라 구현체가 달라진다.
- Affirmative(긍정)Based - 기본 전략, 하나의
Voter라도 동의하면 인가 - Consensus(합의 - 다수결)Based
- Unanimous(만장일치)Based
AccessDecisionVoter
Authentication 객체가 특정 리소스에 접근하는데 필요한 ConfigAttributes 를 만족하는지 확인. 아래와 같은 API를 제공한다.
boolean supports(ConfigAttribute attribute);
// 접근이 허용되는지 여부를 반환
// 허용 1
// 모르겠다 0
// 불허 -1
int vote(Authentication authentication, S object, Collection<ConfigAttribute> attributes);구현체는 여러 가지가 있고, 기본 구현체는 WebExpressionVoter 이다. 이 Voter는 ROLE_Xxx 가 일치하는지를 확인하게 된다.
AccessDecisionManager 구조
앞서 살펴보았듯 AccessDecisionManager 의 기본 구현체는 AffirmativeBased 이다. AffirmativeBased는 내부적으로 Voter를 사용한다. Voter의 기본 구현체는 WebExpressionVoter이다.
그리고, WebExpressionVoter는 다시 내부적으로 DefaultWebSecurityExpressionHandler 라는 것을 사용하는데, 아래 코드를 통해 여러 가지 인가에 필요한 설정 값들을 여기서 설정하는 것으로 추정할 수 있다.
// DefaultWebSecurityExpressionHandler
private String defaultRolePrefix = "ROLE_";
@Override
protected SecurityExpressionOperations createSecurityExpressionRoot(Authentication authentication, FilterInvocation fi) {
WebSecurityExpressionRoot root = new WebSecurityExpressionRoot(authentication, fi);
root.setPermissionEvaluator(getPermissionEvaluator());
root.setTrustResolver(this.trustResolver);
root.setRoleHierarchy(getRoleHierarchy());
root.setDefaultRolePrefix(this.defaultRolePrefix);
return root;
}WebExpressionVoter 는 아래와 같이 핸들러에서 생성한 정보를 토대로 인가를 진행하는 것으로 보인다.

AccessDecisionManager 커스텀
현재는 /admin 페이지의 권한이 아래와 같이 설정되어 있으므로 ROLE_ADMIN 권한을 가진 사용자만이 해당 페이지에 접근할 수 있다.
.mvcMatchers("/admin").hasRole("ADMIN")그런데 만약 USER만 접근 가능한 페이지가 아래와 같이 존재한다고 하자.
.mvcMatchers("/user").hasRole("USER")현재 설정대로라면 ADMIN 권한만 가진 사용자는 /user에 접근하지 못한다. 하지만 일반적으로 ADMIN 은 USER가 접근 가능한 페이지에도 접근이 가능해야 할 것이다. 이를 가능하게 하기 위해선 여러 가지 방법이 있지만 아래와 같이 위에서 살펴본 DefaultWebSecurityExpressionHandler를 커스텀함으로써 가능하게 할 수 있다.
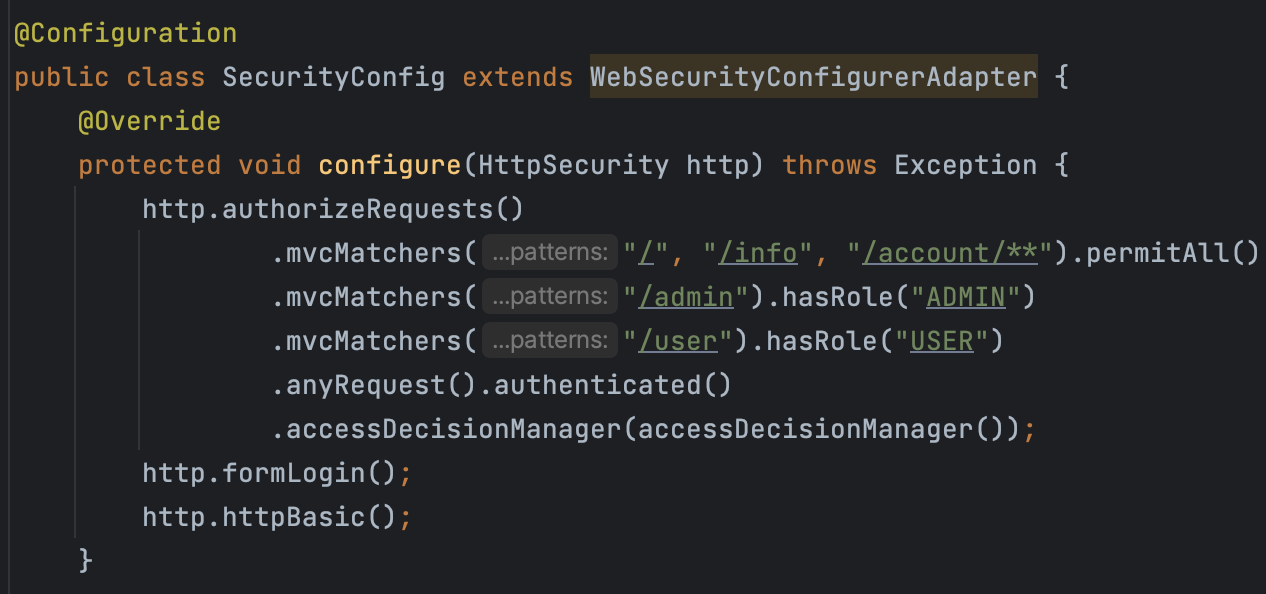
@Configuration
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
public AccessDecisionManager accessDecisionManager() {
// RoleHierarchyImpl 을 사용해 권한 사이의 계층을 명시할 수 있다.
RoleHierarchyImpl roleHierarchy = new RoleHierarchyImpl();
// ADMIN이 USER 보다 상위 계층임을 명시
roleHierarchy.setHierarchy("ROLE_ADMIN > ROLE_USER");
DefaultWebSecurityExpressionHandler handler = new DefaultWebSecurityExpressionHandler();
// 핸들러를 생성해 위에서 만든 RoleHierarchyImpl 정보를 넘겨준다.
handler.setRoleHierarchy(roleHierarchy);
WebExpressionVoter webExpressionVoter = new WebExpressionVoter();
// 위에서 만든 핸들러를 갖는 Voter를 만든다
webExpressionVoter.setExpressionHandler(handler);
// 마지막으로, 위에서 만든 Voter를 갖는 AccessDecisionManager의 구현체 AffirmativeBased를 만들어서 반환한다.
List<AccessDecisionVoter<?>> voters = List.of(webExpressionVoter);
return new AffirmativeBased(voters);
}
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests()
.mvcMatchers("/", "/info", "/account/**").permitAll()
.mvcMatchers("/admin").hasRole("ADMIN")
.mvcMatchers("/user").hasRole("USER")
.anyRequest().authenticated()
// accessDecisionManager()에서 반환하는 커스텀된 AccessDecisionManager를 사용하도록 설정
.accessDecisionManager(accessDecisionManager());
http.formLogin();
http.httpBasic();
}
}FilterSecurityInterceptor
인가 로직 (AccessDecisionManager) 을 호출해주는 필터. 마찬가지로 FilterChainProxy에 의해 호출되며 일반적으로 모든 인증 로직을 마친 후에 인가 여부를 판단하기에 보통 가장 마지막에 실행되는 필터이다.
AbstractSecurityInterceptor 를 상속받고 있으며, 모든 요청이 들어올 때 마다 이 클래스의 아래 로직이 호출되어 인가 여부를 반환하는 decide() 메서드를 호출한다.
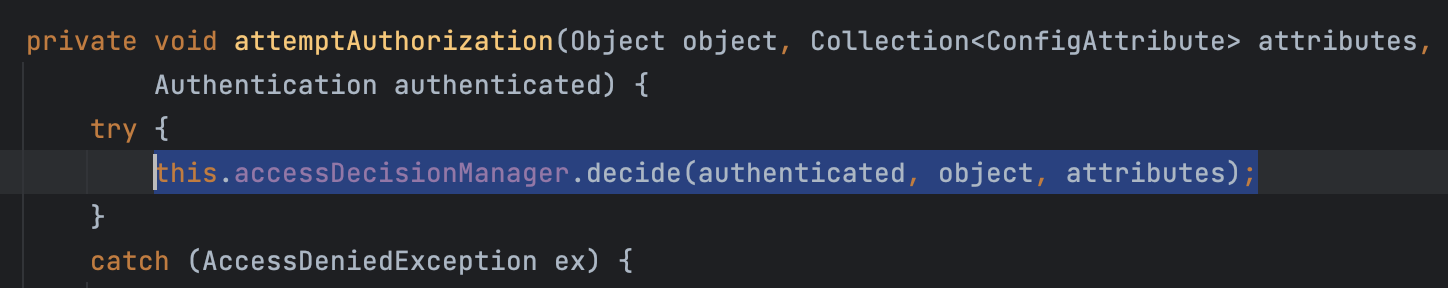
로그인을 하지 않았을 때의 동작
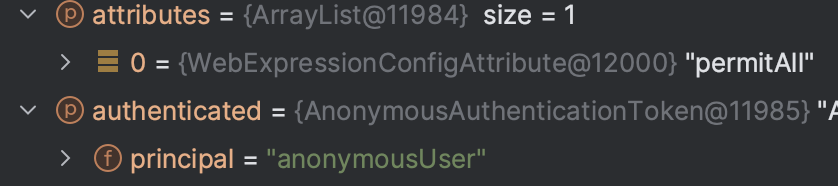
permitAll() 페이지의 경우
아래와 같이 ConfigAttribute가 permitAll 이므로 anonymousUser 임에도 문제없이 페이지에 접근할 수 있다.
권한이 필요한 페이지의 경우
이 경우, ConfigAttribute가 authenticated이므로 anonymousUser 로는 페이지에 접근할 수 없다.
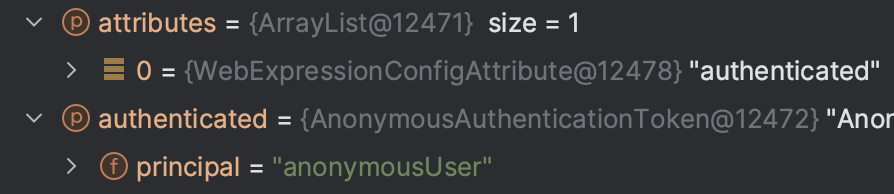
따라서, 아래와 같이 Exception 이 터지고 catch 로직이 수행된다.
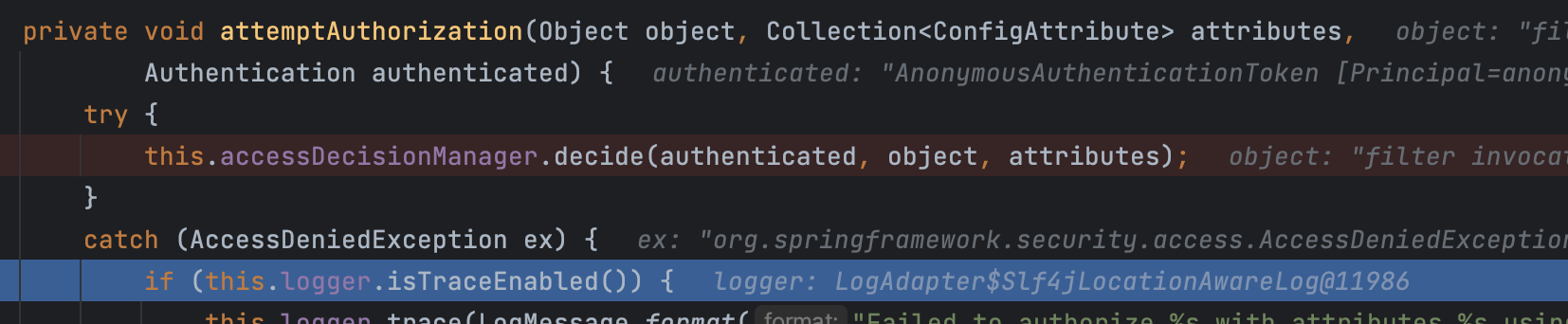
ExceptionTranslationFilter
앞서 권한이 필요한 페이지에 로그인 하지 않고 접속하면 Exception이 발생하고, 로그인 페이지로 이동하게 된다. 이렇게 인증, 인가 실패 등으로 Exception이 터졌을 때 리다이렉션은 누가 어떻게 처리하는걸까?
ExceptionTranslationFilter는
AccessDeniedException과AuthenticationException을 처리한다.
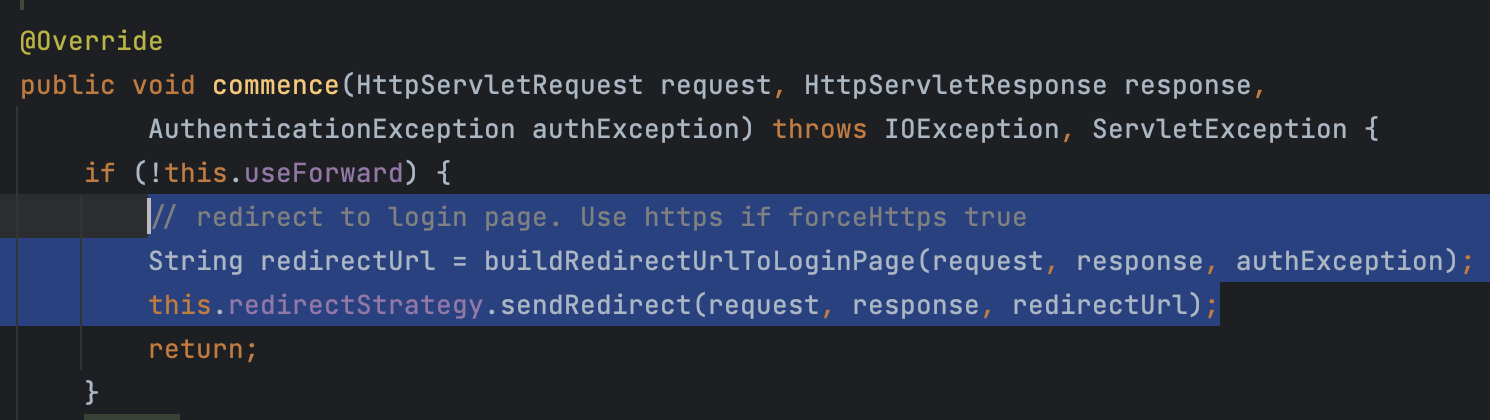
AuthenticationException
인증에 실패했을 때 발생하는 예외로, AuthenticationEntryPoint 를 실행한다. AbstractSecurityInterceptor 의 하위 클래스에서 발생하는 예외만 처리한다. AuthenticationEntryPoint는 인터페이스로 여러 구현체가 있고 그 중 LoginUrlAuthenticationEntryPoint 는 아래와 같이 로그인 페이지로 리다이렉션하도록 구현되어 있다.
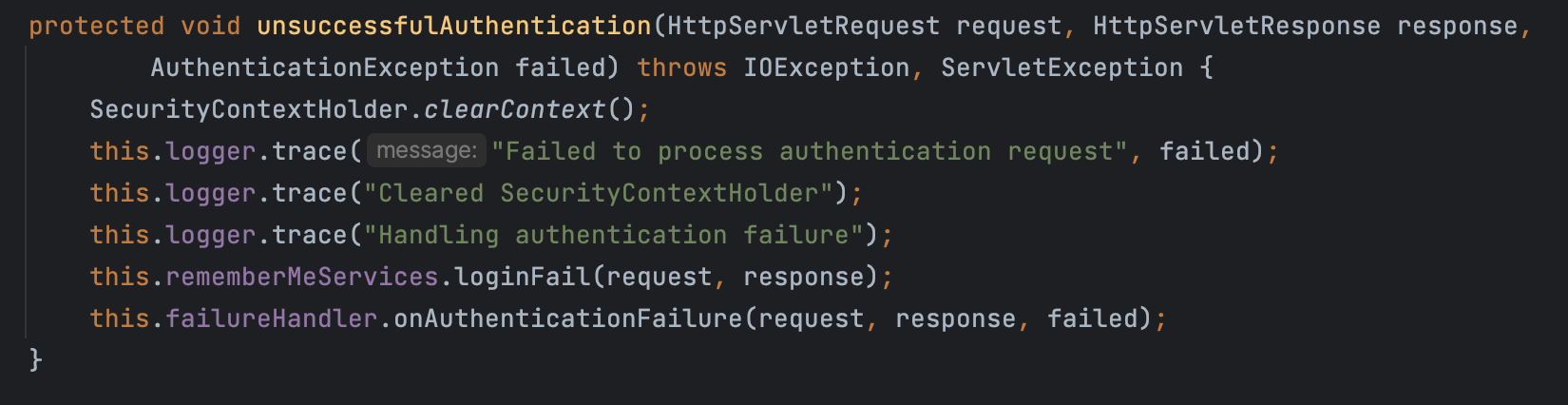
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter 에서 로그인 실패로 발생한 인증 에러는 해당 클래스의 상위 클래스인 AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter(아래 코드) 에서 처리한다.
AccessDeniedException
인가에 실패했을 때 발생하는 오류, 익명 사용자라면 AuthenticationEntryPoint 를 실행하고 아니라면 AccessDeniedHandler 에게 예외 처리를 위임한다.
// class AccessDeniedHandlerImpl implements AccessDeniedHandler
...
@Override
public void handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
AccessDeniedException accessDeniedException) throws IOException, ServletException {
if (response.isCommitted()) {
logger.trace("Did not write to response since already committed");
return;
}
if (this.errorPage == null) {
logger.debug("Responding with 403 status code");
response.sendError(HttpStatus.FORBIDDEN.value(), HttpStatus.FORBIDDEN.getReasonPhrase());
return;
}
// Put exception into request scope (perhaps of use to a view)
request.setAttribute(WebAttributes.ACCESS_DENIED_403, accessDeniedException);
// Set the 403 status code.
response.setStatus(HttpStatus.FORBIDDEN.value());
// forward to error page.
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug(LogMessage.format("Forwarding to %s with status code 403", this.errorPage));
}
request.getRequestDispatcher(this.errorPage).forward(request, response);
}
...WebSecurity
WebSecurity는 기본적으로 WebSecurityConfiguration에 의해 생성되며, DelegatingFilterProxy에서 필터 처리를 위임받는 FilterChainProxy를 생성하는데 사용된다.
아래와 같이 WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter를 상속받아 HttpSecurity 를 인자로 받는 configure 메서드를 재정의하면 시큐리티 관련 설정을 커스텀 할 수 있다. (근데 Deprecated 되어서 다른 방법으로 설정하는 걸 찾아봐야 할 듯함)
질문
서블릿 체인
FilterChain에 여러 개의 필터가 등록되어 있음doFilter()메서드는FilterChain chain을 인자로 받는다. 메서드 내부에서 아래와 같이 작성하면 된다.
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException { /* * 요청 처리 전 수행할 로직 */
}// 체인의 다음 필터 호출 chain.doFilter(request, response); /* * 요청 처리 전 수행할 로직 */필터 vs 인터셉터 (간단히)
- 필터 - J2EE 표준, 디스패처 서블릿 호출 전 / 후로 작동
- 인터셉터 - 스프링에서 제공하는 기능, 디스패처 서블릿이 컨트롤러를 호출하기 전 / 후로 작동

![[플랭고] 스프링 시큐리티 실패 핸들러 에서 직접 예외를 던지면 안 되는 이유](https://img1.daumcdn.net/thumb/R750x0/?scode=mtistory2&fname=https%3A%2F%2Fblog.kakaocdn.net%2Fdn%2Fnr4ue%2FbtsrDgbca1M%2FhJJ3SMr5bFXSIgZRE6l3MK%2Fimg.png)

![[Spring Security] 웹 시큐리티](https://img1.daumcdn.net/thumb/R750x0/?scode=mtistory2&fname=https%3A%2F%2Fblog.kakaocdn.net%2Fdn%2FvwEO4%2Fbtr2ZU4pMw6%2FrdafduHmVavBLMFbDK1mo1%2Fimg.png)
